Plants, much like humans, exhibit signs when they are in distress. However, these signs are often subtle and can be easily overlooked by even the most attentive gardener. Understanding these warning signs is crucial for maintaining the health and vitality of your plants. By paying close attention to changes in your plant’s appearance and behavior, you can address issues before they become severe, ensuring your plants thrive.
Understanding the Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of plant health issues is essential for effective intervention. Just as with human health, catching problems early can prevent more serious complications down the line. By recognizing the early warning signs of distress, gardeners can take corrective action to restore their plants to health. This proactive approach not only saves time and resources but also enhances the overall growth and productivity of the plants.
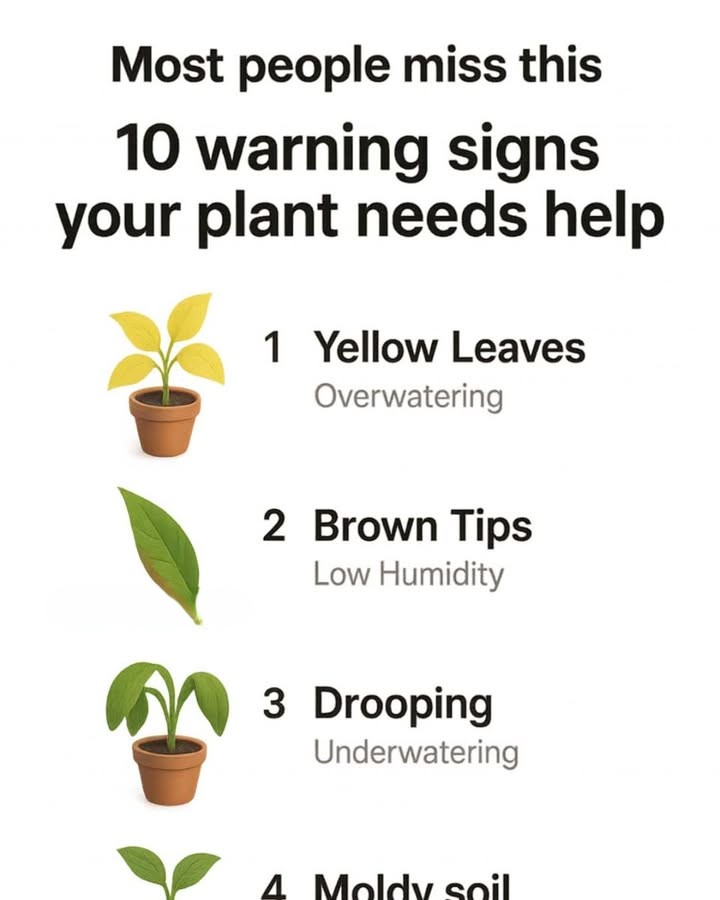
Yellow Leaves: A Sign of Overwatering
Yellowing leaves are often a clear indication that a plant is receiving too much water. Overwatering can lead to root rot, a condition where the roots are unable to absorb oxygen due to waterlogged soil. This lack of oxygen causes the leaves to turn yellow as the plant struggles to survive. To remedy this, ensure your plant’s pot has adequate drainage and allow the soil to dry out between waterings.
Brown Tips: Indicating Low Humidity
When the tips of your plant’s leaves turn brown, it is often a sign of low humidity. Many houseplants, especially tropical varieties, thrive in humid environments. In dry indoor conditions, the lack of moisture in the air can cause the leaf tips to dry out and turn brown. Increasing humidity around the plant by misting, using a humidity tray, or placing a humidifier nearby can help alleviate this issue.
Drooping Leaves: A Result of Underwatering
Drooping leaves are a classic sign that a plant is not receiving enough water. When a plant is underwatered, it cannot maintain the turgor pressure needed to keep its leaves upright, resulting in a droopy appearance. To resolve this, water the plant thoroughly and ensure that the soil is evenly moist. Regularly check the soil moisture to prevent future occurrences.
Moldy Soil: Evidence of Poor Drainage
The presence of mold on the soil surface is a strong indicator of poor drainage. When water cannot properly drain from the soil, it creates a damp environment conducive to mold growth. This can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases. To improve drainage, consider repotting the plant with a well-draining soil mix and ensuring the pot has adequate drainage holes.
Wilting: A Sign of Nutrient Deficiency
Wilting can occur when a plant lacks essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, potassium, or phosphorus. Without these nutrients, the plant cannot perform vital functions, leading to wilting and poor growth. Regularly fertilizing your plants with a balanced fertilizer can help provide the necessary nutrients and prevent wilting.
Next Page